DIY Solar Dehydrator

Preserving food is a crucial issue in many parts of the world, especially in Africa, where food waste and spoilage are common problems. Fortunately, there are cost-effective and sustainable ways to preserve food, such as using a solar food dehydrator. In this article, we’ll show you how to build your DIY dehydrator for sustainable food preservation in Africa.
Preserving food is a challenge, where food waste and spoilage are common problems. Many households lack access to refrigeration or electricity, making it difficult to preserve excess produce or create healthy snacks.
A solar dehydrator is an ideal solution, as it uses the power of the sun to dry food without the need for electricity or gas. In this article, we’ll show you how to build your DIY solar dehydrator for sustainable food preservation in Africa.
Planning and Designing a Solar Food Dehydrator
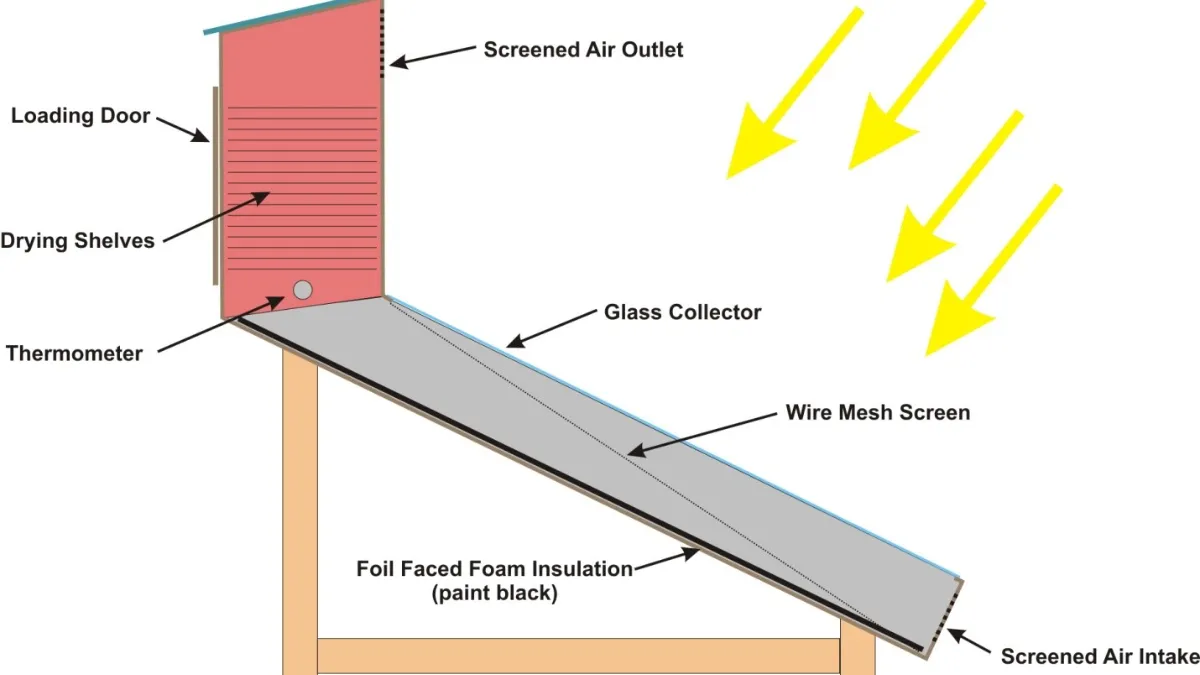
Before you start building your solar homemade dehydrator, you’ll need to consider a few key factors. These include selecting the right materials, designing the unit for maximum sun exposure and air flow, and choosing an appropriate size for your needs.
Materials: Some of the materials you’ll need to build a solar dehydrator include wood, screws, and glazing (such as plexiglass). You’ll also need to select appropriate insulation material.
Design
A good solar food dryer design maximizes sun exposure and airflow to ensure that food dries evenly and quickly. A box-like design with a sloped glazing surface is the most common, but you can also find plans for dehydrators with different shapes and configurations. Many people just simply use window screen materials available at nearby hardware stores.
Size
The size of your solar dehydrator will depend on the amount of food you plan to preserve and the space you have available. A larger dehydrator will allow you to process more food at once, but may require more materials and a larger storage space.
Construction
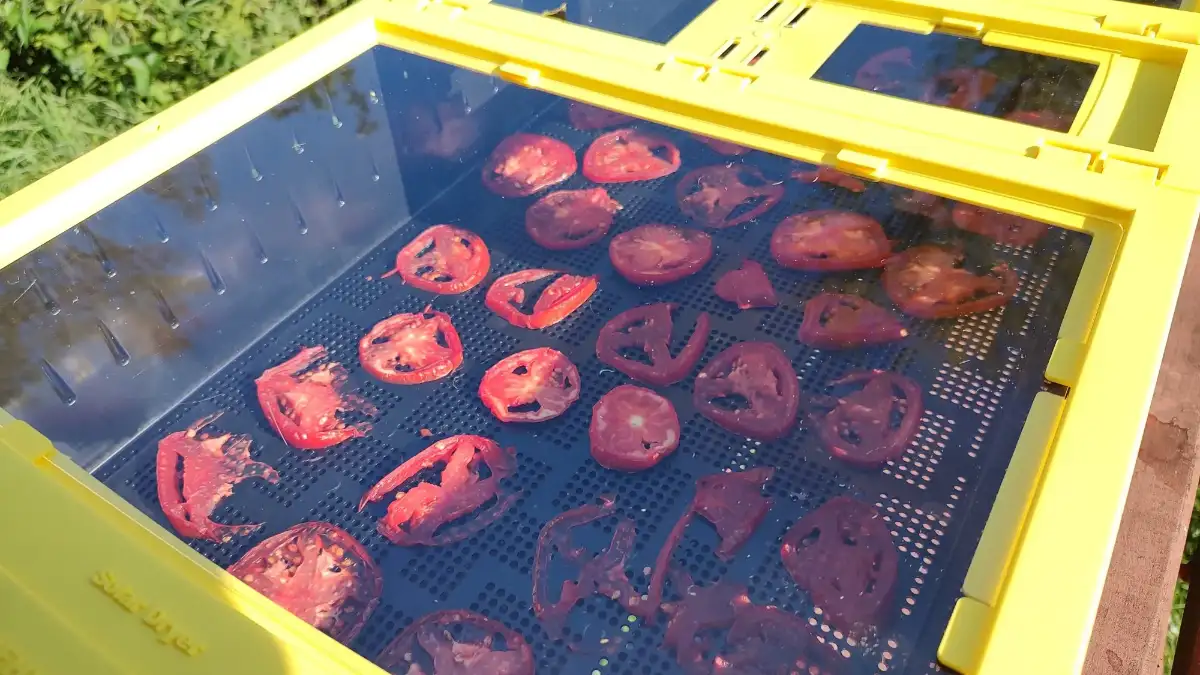

Once you’ve planned your solar dehydrator, it’s time to start building it. Here are the steps you’ll need to follow:
Build the Frame
Begin by building a sturdy frame using the wood and screws. Make sure the frame is level and square. Using power tools , and a circular saw can save you lots of time and effort.
Add the Drying Racks
Install the drying racks inside the frame, leaving enough space between them for air flow. You can use wire mesh or screen to create the racks.
Install the Glazing
Install the glazing on the top of the frame using screws or brackets to hold it in place. Make sure the glazing is sloped to maximize sun exposure.
Add Insulation
Add insulation material to the sides of the frame to keep the heat inside. This will help the food dry more quickly and efficiently.
Paint the Frame
Paint the frame with non-toxic, weather-resistant paint to protect it from the elements.
Testing and Optimization
Once your solar dehydrator is built, it’s important to test its efficiency and optimize its performance. Here are some tips:
Check the temperature and humidity levels regularly to make sure they’re optimal for drying food. The ideal temperature range is between 95-145°F (35-63°C), and the humidity level should be between 30-50%.
Monitor the food drying time to make sure it’s consistent. This will depend on the type of food being dehydrated, but a good rule of thumb is to dry food until it’s crispy and no longer pliable. Prepare and handle your food properly to ensure food safety.
Benefits of Using a Solar DIY Dehydrator in Africa
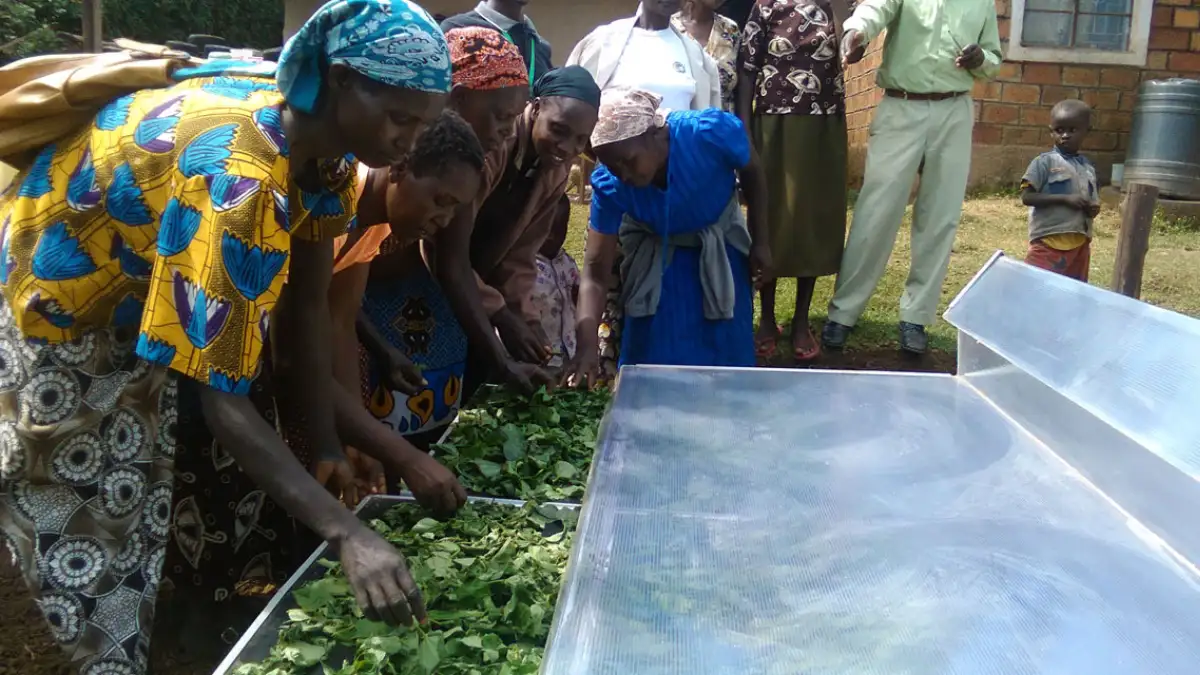

Using a solar dehydrator in Africa has many benefits beyond just preserving. Here are some of the key benefits:
Cost-Effectiveness
Solar food dehydrators are a cost-effective way to preserve food without the need for electricity or gas. This can save money for households and small-scale farmers on groceries and reduce their dependence on non-renewable resources. Additionally, solar dehydrators can be made with locally available materials, reducing the cost of construction and making it accessible to more people.
Health
Solar dehydrators allow for the creation of healthy, preservative-free snacks that are free from additives and other harmful chemicals. This is particularly important in regions where there may be limited access to processed or packaged foods.
Furthermore, solar dehydration allows for the preservation of fruits and vegetables in their nutrient-rich and vitamin-filled state, meaning that people can consume healthier snacks year-round. This can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Sustainability
Using an effective dehydrator is a sustainable way to preserve food and reduce waste. By using renewable energy to dry food, households and small-scale farmers can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Additionally, solar dehydration reduces the need for refrigeration and packaging, which also contributes to a more environmentally-friendly food system. This can help to mitigate the impact of climate change and promote sustainable agriculture practices.
Income Generation
By using solar dehydrators, small-scale farmers can transform their excess produce into value-added products, such as dried fruits and vegetables, which can then be sold in local markets. This provides an additional source of income and supports local economies.
Furthermore, by preserving their excess produce, farmers can reduce their post-harvest losses and improve their overall profitability.
Food Security
By preserving excess produce, solar dehydrators can help households and communities ensure a steady supply of food year-round. In regions where there may be limited access to fresh produce, solar dehydration can also help bridge the gap and ensure that people have access to a variety of fruits and vegetables. This can have a significant impact on the food security of individuals and communities, particularly in areas where access to food is limited.
Climate Adaptation
In regions where climate change is having an impact on agricultural production, solar dehydrators can provide a way to preserve excess produce during times of plenty for consumption during times of scarcity. This can help communities adapt to changing weather patterns and reduce the risk of food shortages during droughts or floods. Additionally, by using renewable energy to preserve food, solar dehydrators can reduce the reliance on non-renewable resources and promote more sustainable agricultural practices.
Challenges and Solutions for Using Solar Dehydrators in Africa
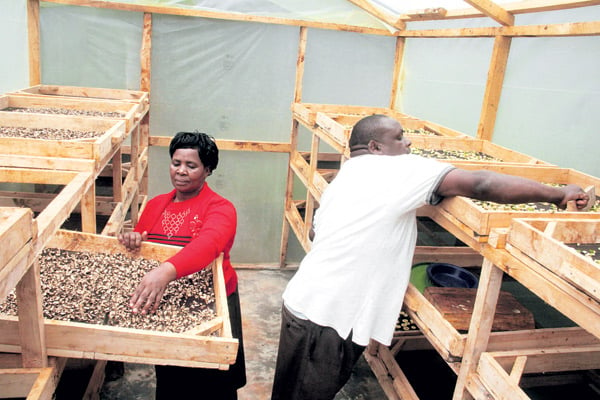

While solar dehydrators have many benefits for sustainable food preservation in Africa, some challenges need to be addressed. These include:
Limited access to materials
Many households and small-scale farmers in Africa may have limited access to materials needed to build a solar dehydrator. To address this, alternative materials or design modifications may be needed.
Variable weather conditions
The effectiveness of a solar dehydrator depends on the availability of sunlight, which can be variable in different regions and seasons. To address this, solar dehydrators may need to be designed with adjustable or mobile glazing to maximize sun exposure.
Food safety concerns
Proper food handling and hygiene practices must be followed to ensure that the food is safe to eat. This may include washing produce before dehydrating and using a food-safe disinfectant to clean the drying racks and glazing.
Conclusion
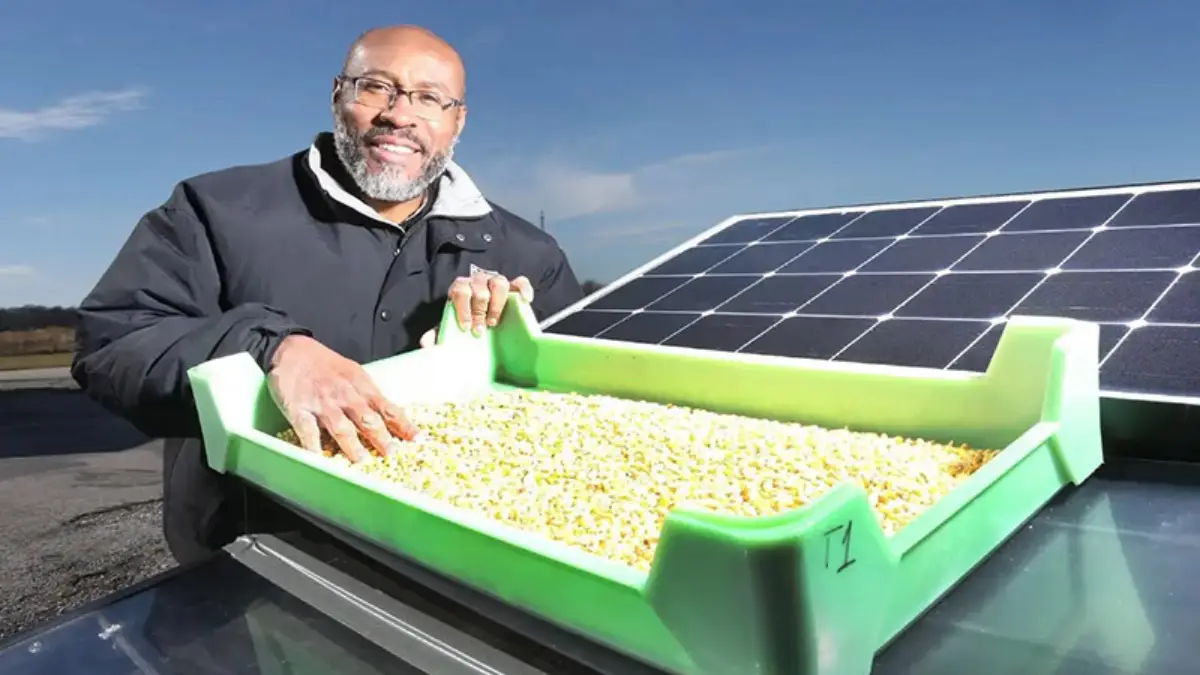

Building a DIY solar dehydrator is a cost-effective and sustainable way to preserve food and reduce waste in Africa. By using the power of the sun to dry food, households and small-scale farmers can create healthy, preservative-free snacks and reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources.
However, it’s important to address the challenges associated with using solar energy in Africa, such as limited access to materials and variable weather conditions. With some effort and ingenuity, solar dehydrators can help promote sustainable food preservation and support a more resilient and self-sufficient food system in Africa. The Impact of Solar power can be great in Africa.





